cervical hyperextension compression test|What is the best way to apply the Spurling test for cervical : convenience store This summary contains information on use of the Spurling test in patients or clients with cervical radiculopathy and other upper extremity nerve pathologies. ICF Domain (s): Body structure and function. ICF Categories: . Banheira. Estacionamento no local. Tem direito a um desconto Genius em Hotel São Gotardo! Só tem de iniciar sessão para poupar neste alojamento. Hotel São Gotardo situa-se em Itamonte, a 38 km de Estádio Municipal Antônio Corrêa e a 16 km de Pico das Agulhas Negras, e dispõe de acomodações com acesso Wi-Fi gratuito, um jardim com .
{plog:ftitle_list}
13 de out. de 2023 · At Eurogrand, you’ll find many popular deposit methods available, including Visa, MasterCard, PayPal, Paysafecard, Instadebit, Poli, SoFort, Nordea, and Neosurf, among others. How to .
The test is positive for cervical radiculopathy if axial loading to the top of the patient's head reproduces the characteristic pain and radicular features. A modification of the . The Spurling test helps to diagnose cervical radiculopathy. It’s also called the Spurling compression test or Spurling maneuver. The Spurling test helps a healthcare provider diagnose cervical radiculopathy (a pinched nerve in your neck). You might need this test if you have pain, numbness or muscle . This summary contains information on use of the Spurling test in patients or clients with cervical radiculopathy and other upper extremity nerve pathologies. ICF Domain (s): Body structure and function. ICF Categories: .
The Spurling test is a diagnostic maneuver used to assess cervical nerve compression and radiculopathy. By reproducing or worsening symptoms through specific .
Special Test: Spurlings Test Purpose: To test for: Compression of a cervical nerve root or facet joint irritation in the lower cervical spine. VIDEO DEMO, Technique, POSITIVE SIGN: .
The Spurling Test is designed to reproduce symptoms by compression of the affected nerve root. The cervical extension is used to induce/reproduce posterior bulging of the .
Oblique views made in flexion and in hyperextension reveal which position causes the greatest antero-posterior alteration or narrowing of the foramina. Antero-posterior .Whenever cervical radiculopathy is suspected our observations suggest the staged provocative maneuvers that should be included in the physical evaluation are extension and lateral .
Defined by hyperextension of the upper cervical vertebrae and forward translation of the cervical vertebrae. . Can lead to a painful shortening of the muscles of the back of the neck, as well as compression of the cervical . Many provocative tests can be used for the cervical spine. The anatomic structures commonly tested are dural tension, foraminal and vertebral canal patency, and muscle, tendon, or ligamentous injuries ().During .
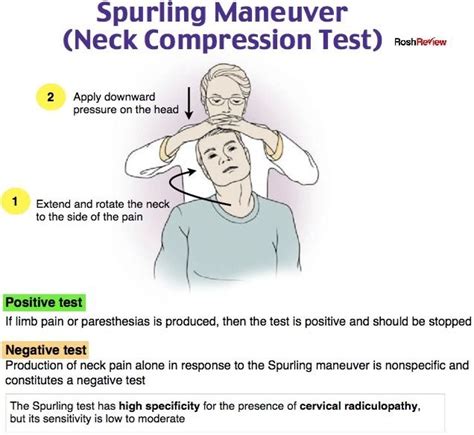
foraminal compression test that is specific, but not sensitive, in diagnosing acute radiculopathy. performed by rotating head toward the affected side, extending the neck, and then applying and axial load (downward .
(2,3) The test is most commonly defined in current literature as passive cervical extension, ipsilateral rotation, and axial compression. (4) This summary contains information on use of the Spurling test in patients or clients with cervical radiculopathy and other upper extremity nerve pathologies.The Kemp test (also known as the quadrant test and extension-rotation test) is a provocative test useful for diagnosing pain related to facet joint pathology, e.g. osteoarthritis.. The client performs combined extension and rotation of the spine (used for the cervical spine or the lumbar spine).; The test is considered positive when the patient reports pain, numbness or tingling in . The cervical spine is a dynamic structure tasked with protecting nervous innervation to the entire body while also maintaining a range of motion for the head and neck. Fractures of the cervical spine are a leading cause of mobility and mortality in trauma patients, and a bone fracture is associated with 56% of cervical spinal cord injuries. Fractures of the .
Additionally there will be hyper-extension of the upper cervical spine with excessive flexion and anterior shear of the lower cervical spine. If there is a deficit in deep extensor muscle strength corrective exercises to resolve stability muscles to normal should be taught and prescribed, potentially facilitating chronic neck pain resolution.• Brachial Plexus Tension Test • Cervical Flexion (including Brudzinski’s Sign, Lhermitte’s sign, Lindner’s sign) • Cervical Flexion Rotation Test • Cervical Compression, Jackson’s Compression, Maximum Foraminal Compression(Spurling’s) • Cervical Distraction • Cervical Resisted Muscle Tests and Passive Range of Motion (O .The diagnostic validity of the cervical flexion-rotation test in C1/2 related cervicogenic headache. Man Ther 2007;12:256-262; ↑ 4.0 4.1 Smith et al. The influence of age, gender, lifestyle factors and sub-clinical neck pain on the cervical flexion-rotation test and cervical range of motion. Manual Therapy 2008;13:552-559
http://citrusparkchiropractic.comDr. Wallace Wade of Citrus Park Chiropractic describes chiropractic tests.Dr. Wade practices chiropractic in Citrus Park Tam. Cervical spine injuries, although uncommon, can result in significant and long-term disability. The cervical spine encompasses seven vertebrae and serves as a protection to the spinal cord.[1][2][3] The segment of the spine most susceptible to injury is the cervical spine based on its anatomy and flexibility. Most commonly, CCS is caused by hyperextension of your neck (moving your head back too far) during a traumatic event (like a fall) in the presence of cervical spinal canal stenosis (narrowing of your spinal canal). What are the symptoms of central cord syndrome? Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture . (hyperextension injury) e.g. patient rear-ended at high speed (hyperextension injury) . manual inline traction should be applied whenever cervical immobilization is removed for securing airway. seat belt sign (abdominal ecchymosis) should raise suspicion for flexion distraction injuries of .
Purpose: To determine if the lumbar spine is the source of the patient's symptoms. Test Position: Sitting. Performing the Test: The patient's arms are folded across his/her chest. The examiner places the lumbar spine in hyperextension (the examiner may choose to maintain the hyperextension by placing his/her knee against the lumbar spine), along with combined .Cervical myelopathy is a condition involving compression of the spinal cord at the cervical level of the spinal column resulting in spasticity, hyperreflexia, pathologic reflexes, digit/hand clumsiness, and/or gait disturbance.. The . All the patients had an anomalous vertebral artery. All had subclavian-vertebral arteriograms preoperatively. Each patient showed an anomaly of the vertebral artery system which allowed intermittent .Compression of these structures can occur as a result of congenital abnormalities, . Hyperextension neck injury, whiplash; Repetitive stress injuries (repetitive injury most often form sitting at a keyboard for long hours.) .
The most common cause of facet joint disease is degeneration of the spine, also known as spondylosis. Causes: When the degeneration of the joint is secondary to natural wearing and abnormal body mechanics the condition is known as osteoarthritis (OA). The pathophysiology of OA is not entirely understood but is a complex one involving various cytokines and proteolytic . Fig. 6.3 SLIC classification for compression injuries: Simple compression morphology is identified by a visible loss of height in the anterior column (a).Compression may be accompanied by definite DLC disruption (b) or laminar fractures (c).Nondisplaced lateral mass and/or facet fractures are also compression injuries (d).Axial view of lateral mass fracture .
Whiplash injuries, commonly associated with rear-end car accidents, involve rapid hyperflexion followed by hyperextension of the neck. This sudden and forceful movement can cause damage to the muscles, ligaments, and discs in the cervical spine, resulting in pain and stiffness. Poor Posture
The mechanical compression on vertebral artery from spurs of the Luschka joint was considered as a main mechanism. The reduction of vertebral artery flow can be more obvious with the rotation and hyperextension of the head. 4 In our current study, we have not found any spur compression on vertebral artery. In addition, mechanical compression .Cervical rib also known as "neck rib" or "supernumerary rib in cervical region" is an extra rib . Thoracic outlet syndrome due to compression of the lower trunk of the brachial plexus or subclavian artery. . It is an orthopaedic test used to diagnose a cervical nerve root injury or cervical disc herniation. It is performed by having the .Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Ans: 1h, 2a, 3c, 4f, 5e, 6b, 7d Classification of spinal cord injury is by the mechanism of injury (e.g., flexion, hyperextension, compression injury, flexion-rotation injury), level of injury or skeletal level of injury (e.g., cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral), and the degree of injury (e.g., complete or incomplete [partial . Cervical myelopathy describes a spinal cord compression at the cervical level of the spinal column resulting in spasticity (sustained muscle contractions), hyperreflexia, pathologic reflexes, digit/hand clumsiness, or gait disturbance.[1][2][3] Classically, it has an insidious onset, progressing in a stepwise manner with functional decline. Without treatment, .
Cervical flexion & rotation Cervical hyperflexion Cervical hyperextension Compression injuries. . Neurological System Patho test 3. 29 terms. megannowezki. Preview. HA. 79 terms. andrewde_gala7. Preview. Management of Patients with Neurologic Trauma. 19 terms. schwabacca. Preview. asthma. 32 terms.Magee et al reported poor cervical muscle endurance is one of the clinical findings we find with cervical instability. A good way to test these muscles (the deep cervical flexor muscles, the longus capitis and longus colli) is the craniocervical flexion test (CCFT) which is a test of neuromotor control. The main goal of the test is to apply an . Objective Preexisting severe cervical spinal cord compression is a significant risk factor in cervical hyperextension injury, and the neurological function may deteriorate after a slight force to .
Shrinkage Testing warehouse
Resultado da Além dos resultados da Liga dos Campeões 2023/2024 pode seguir em Flashscore.pt mais de 1.000 competições de futebol de mais de 90 países em todo o mundo! Simplesmente escolha o nome do país no menu da esquerda e selecione a competição (resultados da liga, live score da taça nacional, .
cervical hyperextension compression test|What is the best way to apply the Spurling test for cervical